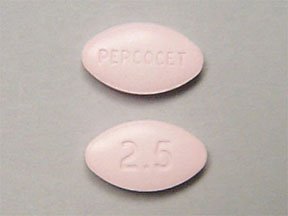
Percocet 2.5/325mg
$304.00 – $654.00
Compare+1 (862) 505-1407 Start Live Chat
Description
What is Percocet 2.5/325mg?
Percocet 2.5/325mg is a prescription medication primarily used for the relief of moderate to severe pain. This formulation combines two active ingredients: oxycodone and acetaminophen. Oxycodone is an opioid analgesic that works by altering the way the brain and nervous system respond to pain. As an opioid, it tends to engage specific receptors in the brain, providing considerable relief from physical discomfort. The acetaminophen component serves as a non-opioid analgesic, enhancing the overall pain-relieving effects and contributing to fever reduction.
The specific dosage of 2.5mg of oxycodone combined with 325mg of acetaminophen characterizes this formulation, indicating its potential strength and efficacy in pain management. It is crucial for patients to adhere to the prescribed dosage, as misuse can lead to significant health risks, including addiction or overdose. The formulation is designed to balance effective pain control while minimizing the risk associated with higher doses of opioids.
Historically, both components have been well-established in medical practice. Oxycodone was first synthesized in 1916 and has been widely used since then for its potent analgesic properties. The introduction of acetaminophen as a safer alternative to more traditional pain relievers dates back to the 1950s. The amalgamation of these two ingredients into one medication, Percocet, created a powerful tool for treating pain in both acute and chronic settings. The FDA approved this combination to offer healthcare providers a versatile option for managing pain while addressing concerns over opioid usage. This careful formulation has allowed the 2.5/325mg variant to remain a relevant choice in the medical community for pain management today.
Indications for Use
Percocet 2.5/325mg is a combination medication primarily indicated for the management of moderate to severe pain. This formulation includes oxycodone, an opioid analgesic, and acetaminophen, a non-opioid pain reliever. The combination is designed to enhance analgesic effects while minimizing the required dose of the opioid component, thereby reducing the risk of dependence and side effects associated with higher doses of opioids.
One of the common indications for prescribing Percocet 2.5/325mg is post-surgical pain. After surgical procedures, patients often experience significant discomfort, and effective pain management is crucial for recovery. Physicians may opt for this medication to provide substantial relief during the acute postoperative period. Similarly, it is frequently prescribed for recovery from injuries, where pain can be moderate to severe, impacting mobility and everyday activities. The dual action of oxycodone and acetaminophen can help address pain while allowing patients to engage in rehabilitation practices promptly.
Moreover, Percocet 2.5/325mg is also indicated for certain chronic pain disorders when other treatments are insufficient. Conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and severe headaches may warrant the use of this medication for effective pain control. Doctors may choose this opioid-acetaminophen blend over other pain relief options, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), particularly when patients have contraindications to NSAIDs due to gastrointestinal, renal, or cardiovascular concerns.
The decision to prescribe Percocet 2.5/325mg is made after careful consideration of the patient’s overall condition, pain severity, and previous responses to pain management therapies. Continuous monitoring is essential to evaluate the effectiveness and address any potential adverse effects as treatment progresses.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
Percocet 2.5/325mg, a combination of oxycodone and acetaminophen, is prescribed for the management of moderate to severe pain. While it can provide effective pain relief, awareness of its potential side effects and risks is crucial for patients. Common side effects associated with Percocet include drowsiness, constipation, nausea, and dizziness. These effects occur as the medication interacts with the brain’s receptors to alleviate pain, often resulting in sedation and gastrointestinal disturbances. Patients should monitor these symptoms and discuss any concerns with their healthcare providers.
More serious risks exist, particularly with prolonged use or when misused. One of the most critical concerns is the potential for respiratory depression, a condition where breathing becomes dangerously slow or shallow. This can result from overdosing or using Percocet in conjunction with other depressants, such as alcohol or benzodiazepines. It is imperative for patients to adhere to prescribed dosages and avoid combining medications without consulting a healthcare professional.
Dependency and addiction are also significant risks associated with the long-term use of opioids like oxycodone. Patients may develop tolerance, requiring higher doses to achieve the same pain relief, which can lead to an increased likelihood of misuse. Furthermore, discontinuing the drug may lead to withdrawal symptoms, emphasizing the importance of managing cessation under medical supervision.
Patient education is essential in mitigating these risks. Individuals prescribed Percocet should engage in open discussions with their healthcare providers about potential side effects, risk factors, and strategies to manage pain effectively while minimizing risks. By fostering this dialogue, patients can make informed decisions regarding their treatment options and overall safety.
Guidelines for Safe Use
When using Percocet 2.5/325mg, it is crucial to adhere to the prescribing physician’s instructions closely. This medication, which combines oxycodone and acetaminophen, is designed to relieve moderate to severe pain and should be taken strictly as directed to minimize the risk of side effects and dependency. The prescribed dosage typically takes into account factors such as age, weight, and overall health. Patients should not adjust their dosages or combine Percocet with other medications without prior consultation with their healthcare provider.
Recognizing the signs of misuse is one of the essential aspects of safe Percocet use. Symptoms may include taking more than the prescribed amount, using the medication for reasons other than pain relief, or experiencing cravings for the medication. It is imperative for patients to maintain open lines of communication with healthcare professionals regarding any potential misuse or concerning habits they may observe. In addition, the reporting of other medications and health conditions is vital, as certain drugs and medical histories may interact adversely with Percocet.
In the event of a missed dose, patients should take the forgotten dose as soon as they remember unless it is close to the time of the next scheduled dose. Under no circumstances should they take extra medication to compensate for a missed dose. If an overdose is suspected, characterized by symptoms such as extreme drowsiness, confusion, or difficulty breathing, immediate medical attention should be sought. It is essential for patients to be informed about the importance of their healthcare providers in managing their treatment, ensuring that all medications are monitored, and that any potential interactions or issues are addressed promptly.
Alternatives to Percocet
When considering alternatives to Percocet, it is essential to recognize that various medications and therapies exist that can effectively manage pain without the potential risks associated with opioid use. One of the prominent non-opioid pain relievers is acetaminophen, which can alleviate mild to moderate pain and is often recommended in conjunction with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen or naproxen. These options demonstrate efficacy for conditions such as arthritis or chronic pain syndromes, providing relief with a lower risk of addiction.
In addition to pharmacological options, non-medication strategies can play a significant role in pain management. Physical therapy is one such approach, as it emphasizes movement and exercise to strengthen the body, improve flexibility, and reduce pain over time. A trained physical therapist can tailor a program that addresses specific pain issues, often resulting in improved function and quality of life. Furthermore, modalities like massage therapy, acupuncture, and yoga have gained popularity for their potential to alleviate pain and promote relaxation, demonstrating the growing recognition of holistic methods in pain management.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) also represents a beneficial alternative. By focusing on the psychological aspects of pain, CBT can help patients develop coping strategies, thus allowing them to manage their pain more effectively. This approach highlights the importance of addressing the individual’s mental and emotional state alongside physical pain, creating a comprehensive treatment plan that goes beyond just medication.
Incorporating a multi-faceted approach to pain relief not only reduces reliance on opioids but also promotes overall wellness. Patients are encouraged to discuss with healthcare professionals the most appropriate combination of treatments tailored to their specific needs, ensuring a safe and effective journey toward pain management.
Additional information
| Pills | 120, 180, 240, 300, 60 |
|---|
6 reviews for Percocet 2.5/325mg




Kayden (verified owner) –
Very well worth the money.
Avery (verified owner) –
Good quality.
Ryan (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery.
David (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery.
Samuel (verified owner) –
Very well worth the money.
Aiden (verified owner) –
Very fast delivery.